Tesla Adds Titanium Underbody Shield and Aluminum Deflector Plates to Model S March 27, 2014 23:19
By Elon Musk, Chairman, Product Architect & CEO
In 2013, two extremely unusual Model S collisions resulted in underbody damage that led to car fires. These incidents, unfortunately, received more national headlines than the other 200,000 gasoline car fires that happened last year in North America alone. In both cases, the occupants walked away unharmed, thanks to the car’s safety features. The onboard computer warned the occupants to exit the vehicles, which they did well before any fire was noticeable. However, even if the occupants had remained in the vehicle and the fire department had not arrived, they would still have been safely protected by the steel and ceramic firewall between the battery pack and the passenger compartment.
It is important to note that there have been no fire injuries (or serious, permanent injuries of any kind) in a Tesla at all. The odds of fire in a Model S, at roughly 1 in 8,000 vehicles, are five times lower than those of an average gasoline car and, when a fire does occur, the actual combustion potential is comparatively small. However, to improve things further, we provided an over-the-air software update a few months ago to increase the default ground clearance of the Model S at highway speeds, substantially reducing the odds of a severe underbody impact.
Nonetheless, we felt it was important to bring this risk down to virtually zero to give Model S owners complete peace of mind. Starting with vehicle bodies manufactured as of March 6, all cars have been outfitted with a triple underbody shield. Tesla service will also retrofit the shields, free of charge, to existing cars upon request or as part of a normally scheduled service.
During the course of 152 vehicle level tests, the shields prevented any damage that could cause a fire or penetrate the existing quarter inch of ballistic grade aluminum armor plate that already protects the battery pack. We have tried every worst case debris impact we can think of, including hardened steel structures set in the ideal position for a piking event, essentially equivalent to driving a car at highway speed into a steel spear braced on the tarmac.
We believe these changes will also help prevent a fire resulting from an extremely high speed impact that tears the wheels off the car, like the other Model S impact fire, which occurred last year in Mexico. This happened after the vehicle impacted a roundabout at 110 mph, shearing off 15 feet of concrete curbwall and tearing off the left front wheel, then smashing through an eight foot tall buttressed concrete wall on the other side of the road and tearing off the right front wheel, before crashing into a tree. The driver stepped out and walked away with no permanent injuries and a fire, again limited to the front section of the vehicle, started several minutes later. The underbody shields will help prevent a fire even in such a scenario.
The first of the three shields is a rounded, hollow aluminum bar that is designed to either deflect objects entirely or, in the case of a self-stabilizing, ultra high strength object, like a three ball steel tow hitch, absorb the impact and force it to pike upwards well forward of the battery pack. This pierces the plastic aeroshield and front trunk liner, but causes no damage affecting safety and the car remains in control and driveable before, during and after the impact.
This is followed by a titanium plate, which has exceptional strength-to-weight properties and is more commonly seen in aerospace or military applications. The titanium plate prevents sensitive front underbody components from being damaged and aids in neutralizing the road debris.
By this point, the vast majority of objects will have been deflected or crushed. For the rare piece of debris that remains intact, we added a third shield, which is a shallow angle, solid aluminum extrusion that further absorbs impact energy, provides another layer of deflection and finally causes the Model S to ramp up and over the object if it is essentially incompressible and immovable.
Thanks to high speed cameras fixed underneath the cars during testing, we have a close-up view of what happens to the objects on impact. As illustrated in the slow motion videos below, the shields destroy everything from a solid concrete block to a steel alternator and safely capture and eject objects made of ultra-hard steel.
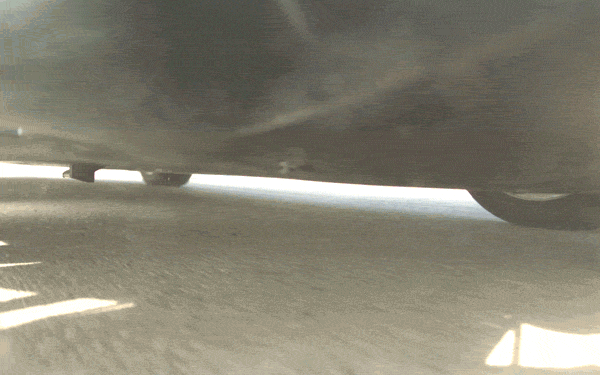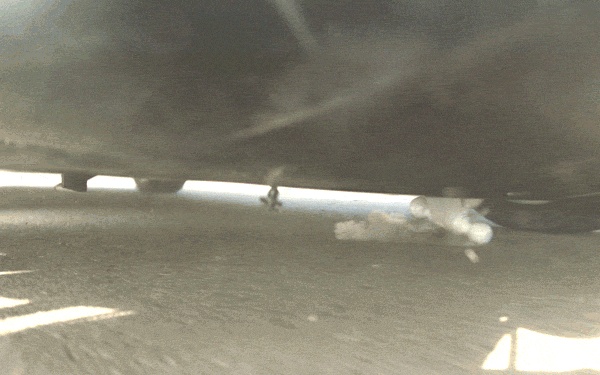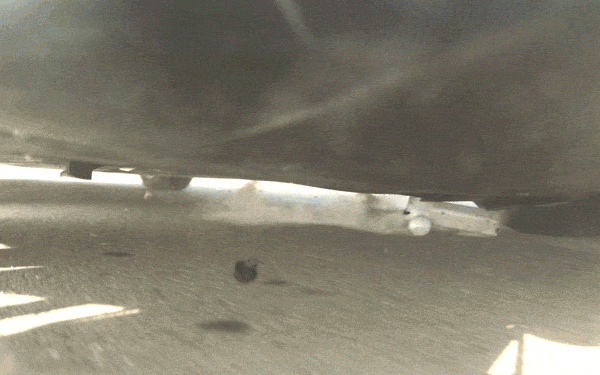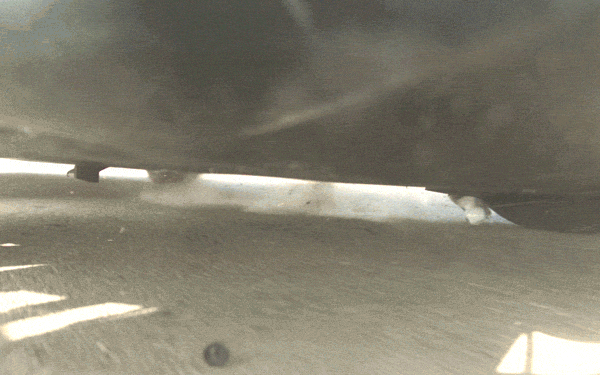


The protective qualities of the underbody shields are substantial, but their effect on the overall structure of the vehicle is minimal. In total, the shields only have a 0.1 percent impact on range and don’t affect ride or handling. Wind tunnel testing shows no discernible change in drag or lift on the car.
As the empirical evidence suggests, the underbody shields are not needed for a high level of safety. However, there is significant value to minimizing owner inconvenience in the event of an impact and addressing any lingering public misperception about electric vehicle safety. With a track record of zero deaths or serious, permanent injuries since our vehicles went into production six years ago, there is no safer car on the road than a Tesla. The addition of the underbody shields simply takes it a step further.
- Elon
